How To Build An E-commerce App: A Step-by-Step Guide
2025-08-20 08:54:11
The e-commerce market has been on an unstoppable rise since 2010, experiencing exponential growth during the COVID-19 pandemic. With over five billion internet users worldwide, online shopping has become the new normal. According to Statista forecasts, global retail e-commerce sales are projected to exceed 4.3 trillion U.S. dollars by 2025—and this figure will continue to climb in the years ahead.
So for retailers, the real question is no longer “Should I go online?” but rather “How to build an e-commerce app the right way?”
In this step-by-step e-commerce app development guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know to successfully develop an app tailored to your business needs.
What is an E-commerce Mobile App?
An e-commerce mobile app is a digital application built for smartphones and tablets that allows users to browse, purchase, and manage orders seamlessly. Unlike mobile websites, these apps are specifically designed to enhance the mobile e-commerce user experience through faster performance, intuitive navigation, and exclusive features.
Types of E-commerce Apps:
Native Apps: Built for a specific platform (iOS or Android) using platform-specific languages. Offer the best speed, performance, and security.
Hybrid Apps: Cross-platform apps developed using a single codebase. Faster to build but may sacrifice performance compared to native apps.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Web applications that behave like native apps with offline access and push notifications.
Advantages of E-commerce Apps Over Mobile Websites:
Speed & Performance: Apps load faster than mobile websites.
User Experience: Sleeker UI/UX design tailored for mobile usage.
Push Notifications: Drive customer engagement through personalized alerts.
Offline Access: Allow browsing even without an internet connection.
For businesses, building an app isn’t just a trend—it’s a strategic move. A well-planned e-commerce app development project can transform customer engagement, build brand loyalty, and significantly increase sales.
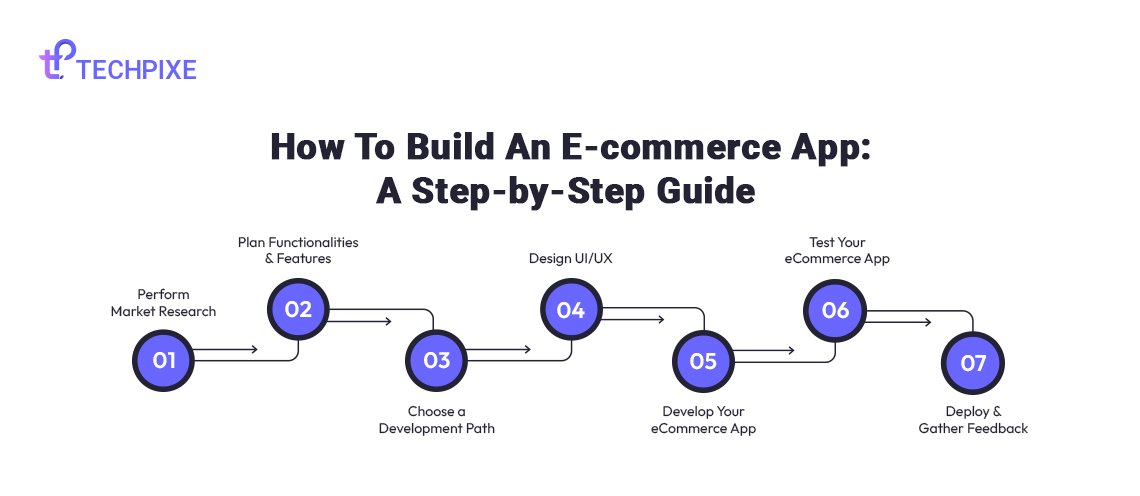
8 Steps of How to Build an E-commerce App
Building an e-commerce app isn’t a one-day task. It involves a structured process. Let’s break it down into 8 essential steps of ecommerce app development:
Step 1: Define Your Niche and Target Audience
The very first step in e-commerce app development is clarity about “who your app is for” and “what problem it solves.”
Market Research: Study industry reports, customer behavior, and e-commerce trends. For example, is your audience looking for affordable everyday items, premium fashion, or niche products like organic skincare?
Competitor Analysis: Identify key players in your niche and analyze their app features, customer feedback, and shortcomings. This gives insights into what customers want but aren’t getting.
User Personas: Create profiles of your target customers. Think age group, income level, shopping habits, and device usage.
Pain Points: Understand where users struggle—slow checkout? Limited payment options? Poor product discovery? Your app should solve these frustrations.
By narrowing down your niche and audience, you avoid building a generic app and instead create one that feels personalized and relevant.
Step 2: Plan Your App’s Functionality and Features
This is where you define the scope of your e-commerce app guide.
List Features: Begin with MVP (minimum viable product) features—login, product catalog, search, cart, and payment gateway. Then, plan for advanced features like AI-driven recommendations, AR previews, and loyalty programs.
Prioritize Features: Rank them based on what’s essential for launch vs. what can be added later.
User Flows: Map out the journey a customer takes—from opening the app to completing a purchase. A smooth user journey is key to conversions.
Wireframing: Sketch basic screens to visualize layout and navigation. This ensures your development team understands how each feature fits into the app.
Planning at this stage prevents costly mistakes during development and ensures the app aligns with user expectations.
Step 3: Design the User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI)
A sleek design is non-negotiable for mobile e-commerce user experience.
E-commerce App Design Best Practices:
Keep navigation intuitive with simple menus.
Reduce checkout steps to prevent cart abandonment.
Use clear product images and easy-to-read fonts.
Keep CTAs (Call to Actions) like “Buy Now” or “Add to Cart” visible.
Mobile-first Approach: Remember, most users shop on their phones. Design with thumb-friendly buttons, responsive layouts, and fast-loading pages.
Prototyping & Testing: Tools like Figma or Adobe XD allow you to create clickable prototypes. Test these with real users before coding to spot UX flaws early.
A well-designed interface directly impacts how much users enjoy the app—and whether they return.
Step 4: Choose Your Tech Stack
Choosing the right tech stack for an e-commerce app determines performance, scalability, and maintenance.
Front-end (User Interface):
Native apps: Swift (iOS), Kotlin/Java (Android).
Cross-platform: React Native, Flutter (saves time, works on both platforms).
Back-end (Server-side Logic):
Node.js, Django, or Ruby on Rails.
Microservices architecture for scalability.
Databases: MySQL, MongoDB, Firebase (choose based on your data needs).
APIs & Integrations:
Payment gateways (Stripe, Razorpay, PayPal).
Shipping APIs (FedEx, UPS).
CRM/ERP for business operations.
Cloud Hosting: AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure for flexibility and high availability.
Your stack should align with long-term goals—avoid short-term fixes that limit scalability later.
Step 5: Begin Development (Front-end & Back-end)
Now comes the actual coding. A professional approach is to use Agile methodology with iterative sprints.
Front-end Development: Translate your wireframes into functional designs. Ensure fast loading, smooth animations, and responsive layouts.
Back-end Development: Build the engine—manage databases, user authentication, product catalogs, and order processing.
Integration: Add third-party services like payment gateways, shipping, and social media login.
Version Control: Use GitHub or GitLab to manage collaborative coding.
At this stage, your app starts to take shape, but frequent testing during development is essential to avoid rework later.
Step 6: Rigorous Testing and Quality Assurance
An e-commerce app can’t afford errors. Even a single bug during checkout may cause lost revenue. Testing ensures reliability.
- What is a Dynamic Website?
Dynamic websites are the ones that keep changing the content or page layout with each request from the user to the web server. Unlike static websute dynamic websites fetch run-time data with each request. This inherent real-time data fetching and providing it to the user makes a website dynamic and not static sites.
Now that we know what a dynamic website is let's understand the types.
Types of Dynamic Websites
There are mainly two types of programming in dynamic website development. One being client-side and the other is related to server. Let's take a look at Client-side scripting.
Client-side Scripting
Client-side scripting basically refers to programming language like JavaScript, which are executed on the user's web browser. These scripts make a webpage more dynamic by enabling it to respond to user input. It interacts with the page without the user having to reload it.
Server-side Scripting
Conversely, server-side scripting refers to programming languages like Ruby, PHP, and Python. These are executed on the web server. These scripts are then used to generate dynamic content for the web page sent to the user's web browser. Tasks like user authentication, database queries, form handling, and submissions are examples of server-side scripting.
Both types of scripting are essential in dynamic website development since there will always be a client and a web server between whom the queries and transactions will take place.
Features of Dynamic Website
A dynamic website can be easily updated and changed, providing various features that make them more engaging than static websites. Some of these features are as follows:
Database driven content
dynamic websites stores data in databases. This enables easy searching, filtering, and information sorting.
CMS (Content Management System)
dynamic websites is governed by a CMS, which lets users easily edit, delete and modify data on the website.
Interactive elements
One can add engaging elements like forms, QnAs, trivia, etc., to the web pages. This makes the website more interactive and exciting.
Dynamic Website Example
There are endless examples of dynamic websites today on the internet like Amazon, Facebook, Airbnb, and Spotify. Other than these, all e-commerce sites, calendars, to-do sites, and any website with information that needs regular updation are all examples of dynamic websites
Conclusion
There are endless examples of dynamic websites today on the internet like Amazon, Facebook, Airbnb, and Spotify. Other than these, all e-commerce sites, calendars, to-do sites, and any website with information that needs regular updation are all examples of dynamic websites
-->
Similar Blogs

Web Design vs. Web Development: What's the Difference and Why It Matters
Web Design vs. Web Development: What's the Difference and Why It Matters
Do you have a project in mind ?
We have the team, tools, and technology to turn
it into reality!


.png)